RFICs
PRODUCTS
-
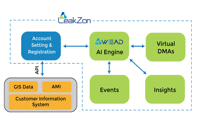
LeakZon provides a powerful and versatile platform that adapts to your water management needs. Whether you oversee a small or large operation, LeakZon scales effortlessly to accommodate your requirements. Our seamless integration with various data sources, including GIS Data, AMI, and Billing (CIS), allows for a holistic view of your water network. This comprehensive data integration empowers you to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and maximize efficiency.
-
Meaningful insights. Better results. Smarter utility management. Trimble Unity software platform offers a suite of applications and tools to support smart water management. Includes advanced workflows to map, manage, measure and improve asset performance.
-
Eurofins PSS Insourcing Solutions® (PSS) is a global, award-winning managed service provider that places our people at your site dedicated to running and managing your manufacturing and laboratory services while eliminating headcount, co-employment and project-management worries.
-
PHCbi brand’s LabSVIFT® IoT lab management solution is designed to provide real-time visibility and control of laboratory equipment and environments across single or multiple facilities. This cloud-based platform enables centralized monitoring, customizable alerts, and secure data access via a web-based dashboard. The new health check* function continuously evaluates equipment performance, identifies irregularities, and provides recommended corrective actions to maintain optimal operation. The system supports FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance and is compatible with select PHCbi and third-party devices. *health check function compatibility varies by model
-
KRYTAR's 4-50 GHz directional couplers are crafted for system applications necessitating external leveling, precise monitoring, signal mixing, or swept transmission and reflection measurements.
WHITE PAPERS AND CASE STUDIES
-
Data Key In Addressing Patient Recruitment Challenges
Explore how a Phase II trial for extensive-stage and previously treated small cell lung cancer overcame recruitment challenges with a data-driven solution designed to surface protocol-matched patients.
-
Responsible Reclamation – City of Abilene, Texas
To combat drought, Abilene, Texas, implemented a reuse system utilizing O3 + BAC to remove trace organics. This solution met strict standards, ensured water resilience, and proved more cost-effective than AOP alternatives.
-
EHR-To-EDC Success In A Complex, Adaptive Platform Trial
I-SPY 2, one of the longest-running adaptive platform trials in oncology, is revolutionizing breast cancer research through a dynamic, data-driven approach to evaluating novel therapies.
-
Mobile Gowning Cleanroom, Built To Meet ISO 7 Requirements
Uncover how Germfree designed and installed a mobile cGMP cleanroom on a 53′ tractor-trailer chassis to provide a flexible and efficient cleanroom solution tailored to the company’s needs.
-
Overcoming HCP Co-Elution Issues Using Cell Line Engineering
Product quality assessments revealed that a customer’s therapeutic protein had a range of hydrophobic HCPs. Review a solution that took an alternative approach by utilizing cell line engineering.
-
Scalable Production Of High-Purity Nanobodies Using Yeast Expression System
Leverage scalable K. pastoris expression systems to produce high-quality nanobodies for cutting-edge therapeutic, diagnostic, and research applications.
-
Automated Trial Monitoring Workflows Make A Lean Team More Efficient
A pharmaceutical therapy developer was looking to automate reports, confirmation letters, and follow-up letters. See what happened when they adopted a cloud-based solution for end-to-end trial management.
-
How Vanguard Clinical Harnesses CDMS/EDC For Faster Results
Uncover how this CRO was able to stay agile by choosing a CDMS/EDC partner that prioritized sponsor needs and streamlined operations to achieve top-tier results swiftly.
-
AMERICAN And Partners Install Boltless Restrained Underwater Pipeline System In Ashland, Wisconsin
Beneath the waters of Chequamegon Bay on Lake Superior in Ashland, Wisconsin, about 4,500 feet of 24-inch AMERICAN Flex-Ring Ductile Iron Pipe and a submerged timber crib intake structure were installed to ensure the city’s residents have quality drinking water for the next 100 years. The Ashland Water Intake Project began May 1, 2025, and is now complete.
-
Overcoming Rapid Growth Challenges With Process Liquid Preparation
With a helpful assessment and the right process liquid preparation services, the CDMO featured in this study was able to find a path toward meeting the surge in demand for a client's therapeutic .
-
Transferring From Microfluidics To A Turbulent Mixer
What solutions did the client featured in this case study find when they sought help in transferring their formulation process to a turbulent Impinged Jet Mixing (IJM)?
-
AI Predictive Maintenance Prevents Batch Loss And Production Shutdown
AI-powered predictive maintenance with wireless vibration sensors prevented costly batch loss and production shutdowns in pharma manufacturing by detecting and fixing equipment issues before failures occurred.
NEWS
-
Puraffinity Signs First Commercial Agreement For Full-Scale Deployment Of Its PFAS Removal Technology6/2/2025
The agreement was signed with Envytech Solutions, the leading expert in mobile water treatment in the Nordic region and a member of the Sortera Group, which operates across the Nordics and the UK.
-
Ovarro Opens New Asia Pacific Headquarters8/27/2025
Water technology provider Ovarro has opened a new Asia Pacific headquarters and production facility in Selangor, Malaysia.
-
Redex Preloaded Systems Deliver Precise Positioning For Machine Tools1/16/2025
Redex is pleased to announce its patented DualDRIVE and TwinDRIVE preloading technologies now give CNC machine designers several ways to build a zero backlash system.
-
New Land Grant Research Detects Dicamba Damage From The Sky7/9/2025
Drones can now detect subtle soybean canopy damage from dicamba at one ten-thousandth of the herbicide’s label rate — simulating vapor drift — eight days after application.
-
Evonik Partners With ST Pharm To Increase Its Offerings For RNA And Nucleic Acid Delivery1/8/2025
Evonik is partnering with ST Pharm, a company that manufactures active ingredients for gene therapy, to expand its RNA and nucleic acid therapeutic services.
ABOUT
About Nutrient Removal
Nutrient removal from wastewater consists of treating wastewater to remove nitrogen and phosphorus before it reenters natural waterways. High levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in wastewater cause eutrophication, a process where excess nutrients stimulate excessive plant growth such as algal blooms and cyanobacteria. The decomposition of the algae by bacteria uses up the oxygen in the water causing other organisms to die. This creates more organic matter for the bacteria to decompose. In addition, some algal blooms can produce toxins that contaminate drinking water supplies.
As authorized by the Clean Water Act, the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permit program regulates point sources, such as municipal wastewater treatment plants, that discharge pollutants as effluent into the waters of the United States. In recent years, many of the States’ environmental bodies have lowered nutrient limits to arrest eutrophication. Maryland’s effort to protect the Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries is perhaps the most notable example of nutrient removal in the US. Nutrient removal continues to be a growing area of focus for wastewater treatment throughout the world.
The removal of nitrogen and phosphorus require different nutrient removal processes. To remove nitrogen, the nitrogen is oxidized from ammonia to become nitrate through a process called nitrification. This process is then followed by denitrification where the nitrate is reduced to nitrogen gas which is released to the atmosphere and removed from the wastewater.
Nitrification is a two-step aerobic process which typically takes place in aeration tanks. Denitrification requires anoxic conditions to encourage the appropriate biological conditions to form. The activated sludge process is often used to reduce nitrate to nitrogen gas in anoxic or denitrification tanks.
Phosphorus can be removed biologically using polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs) which accumulate large quantities of phosphorus within their cells and separate it from treated water. Phosphorus removal can also be achieved by chemical removal. Once removed as sludge, phosphorus may be stored in a land fill. However, many municipalities and treatment facilities are looking to resell the biosolids for use in fertilizer.