Imec And Septentrio Co-Design Antenna For High Precision Global Navigation Satellite Systems
Compact and Low Cost Next-Generation GNSS Antenna Offers Enhanced Positioning for GIS Devices
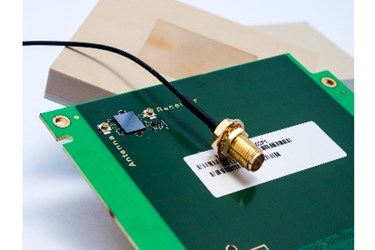
Imec and Septentrio recently announced that they have collaborated to the design of an antenna-RF integrated element of a multi-frequency Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) antenna for GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and GALILEO. Developed under the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme project HANDHELD, the compact antenna can be integrated in multi-frequency handheld GNSS devices for high precision location applications (up to 1 centimeter).
The most prominent satellite navigation system is the United States Global Positioning System (GPS), which, like the Internet, is becoming a Global Information Asset. First generation GPS receivers have an accuracy of a few meters when solely relying on the navigation satellites. Advance in technology and new demands on the existing GPS have led to efforts to modernize and develop other systems such as Russia’s GLONASS, Europe’s GALILEO and China’s BeiDou. So called next generation Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), when combined, aims for higher availability, accuracy and integrity.
Imec and Septentrio co-developed a compact antenna integrating imec’s innovative GNSS antenna and Septentrio’s GNSS RF front-end. Imec’s antenna design satisfies the requirements for the high-accuracy GNSS market while remaining small enough to fit in a handheld surveyor device. The antenna simultaneously receives all GPS, GLONASS and GALILEO bands. It has desired uniform gain and phase coverage over the complete upper hemisphere with strong suppression of unwanted reflected signals below or in the vicinity of the GNSS receiver.
The GNSS RF front-end, based on established market leading front-end technology developed by Septentrio, is characterized by a superb out-of-band interference rejection to avoid notably device self-interference with other radiation sources such as Bluetooth and WLAN radios, as well as other ambient intentional and non-intentional interference. The compact multi-frequency antenna is a perfect companion of Septentrio’s compact and low power AsteRx-m receiver, a credit card-sized dual frequency GNSS receiver that provides centimeter accuracy at less than 500mW power consumption, by far the lowest power consumption in the professional GNSS market.
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n°287183.
About imec
Imec performs world-leading research in nanoelectronics. Imec leverages its scientific knowledge with the innovative power of its global partnerships in ICT, healthcare and energy. Imec delivers industry-relevant technology solutions. In a unique high-tech environment, its international top talent is committed to providing the building blocks for a better life in a sustainable society. Imec is headquartered in Leuven, Belgium, and has offices in Belgium, the Netherlands, Taiwan, US, China, India and Japan. Its staff of over 2,080 people includes more than 670 industrial residents and guest researchers. In 2012, imec's revenue (P&L) totaled 320 million euro. For more information, visit www.imec.be.
About Septentrio
Septentrio Satellite Navigation designs, manufactures, sells and supports high-precision OEM GNSS receivers for the most demanding professional navigation, positioning and timing applications. Septentrio delivers breakthrough technology in the development of high-end GNSS receiver instruments and the integration of hybrid solutions. Septentrio receivers offer unrestricted signal tracking capability and the most comprehensive range of countermeasures to mitigate GNSS vulnerability. For more information, visit www.septentrio.com/products.
Source: Imec
